Recovery from brain concussion by Dān qì medical technique
丹氣醫療技術實現腦震盪的康復
Introduction
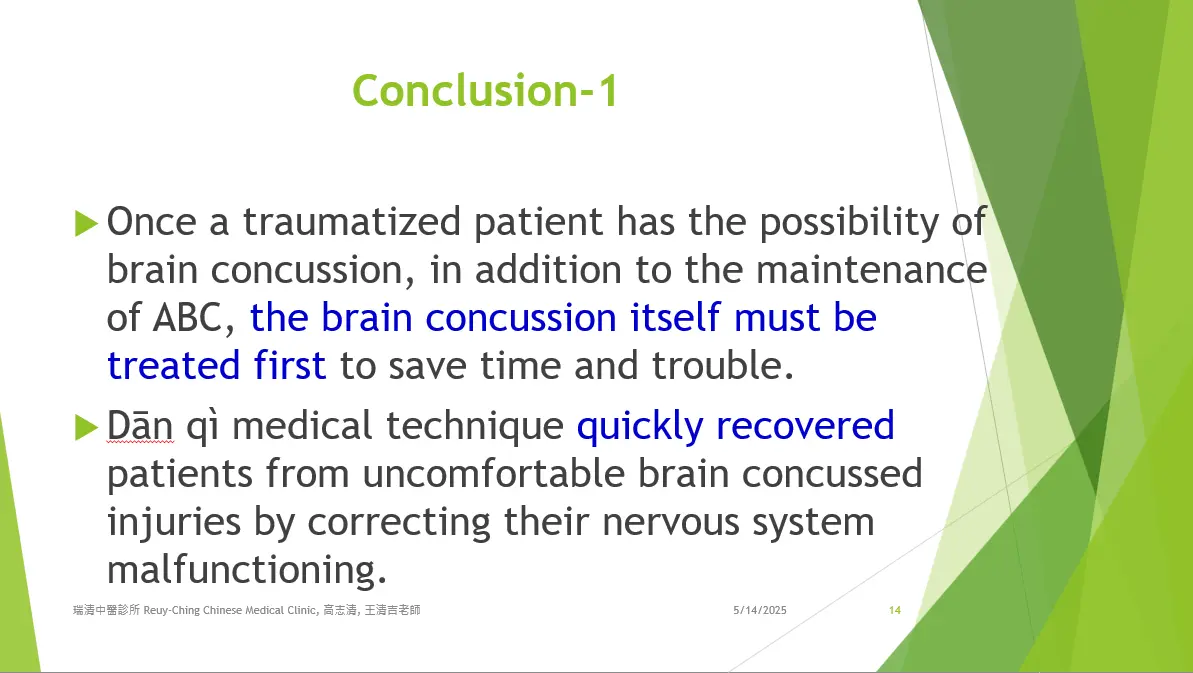
Concussion in patients with head trauma remains a major challenge in diagnosis and treatment. It usually occurs when a direct impact to the head or body transmits force to the brain, causing nervous system dysfunction. Common symptoms include headache, dizziness, nausea, vomiting, body aches, chest tightness, and difficulties with balance, thinking, memory, concentration, or eye focus. Current treatments mainly involve observation, rest, anti-nausea medication, and pain relief. However, patients often continue to experience discomfort for varying lengths of time despite these treatments.
簡介
頭部外傷患者的腦震盪在診斷和治療上仍是一大挑戰。腦震盪通常是因頭部或身體其他部位受到直接撞擊,力量傳導至腦部,導致神經系統功能異常。常見症狀包括頭痛、頭暈、噁心、嘔吐、全身酸痛、胸悶,以及平衡、思考、記憶、注意力或眼睛聚焦困難。目前的治療主要是觀察、休息、止吐藥和止痛藥,但患者即使接受這些治療,仍可能持續感到不適,時間長短不一。
Materials and Methods
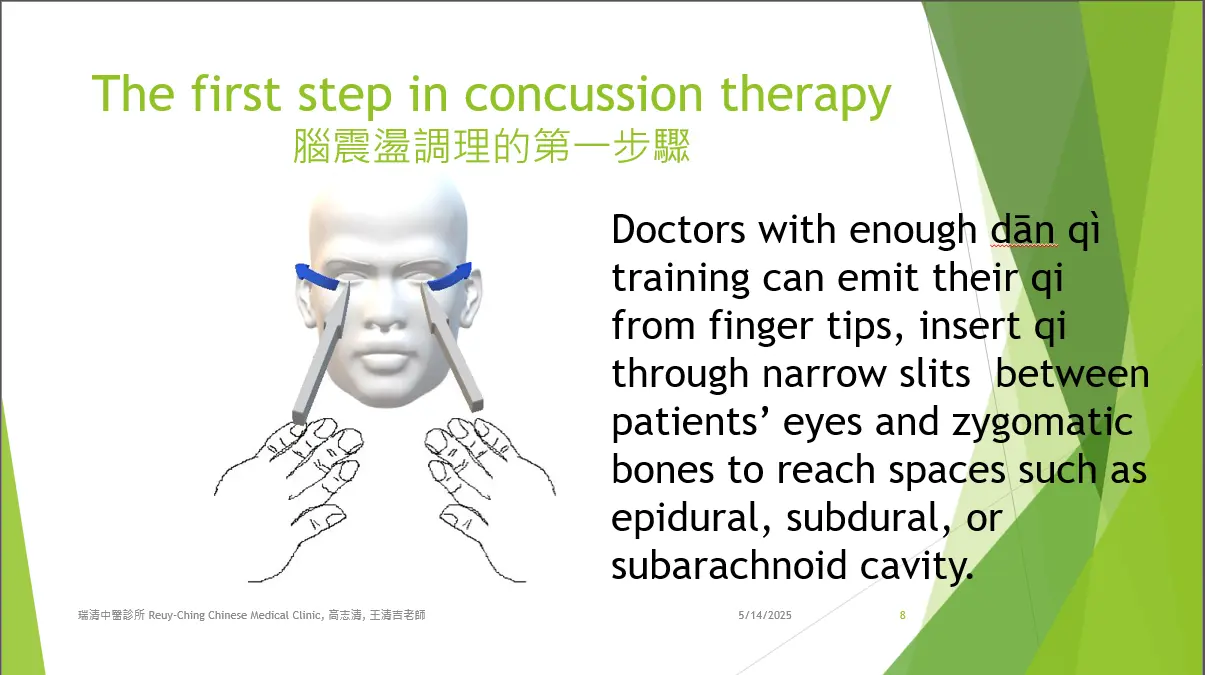
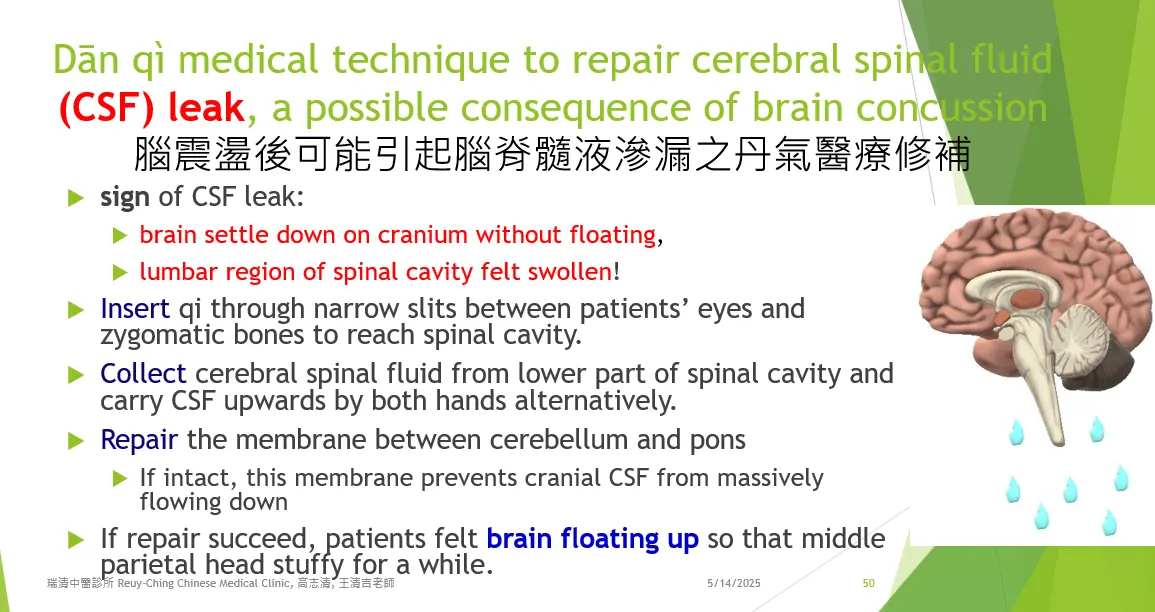
Dān qì medical technique, a branch of traditional medicine, has been passed down through a mentor-apprentice system for many dynasties but is not included in modern medical education. Skilled practitioners can emit qi from their fingertips and guide it through narrow gaps between the patient's eyes and cheekbones to reach spaces such as the epidural, subdural, or subarachnoid cavities.
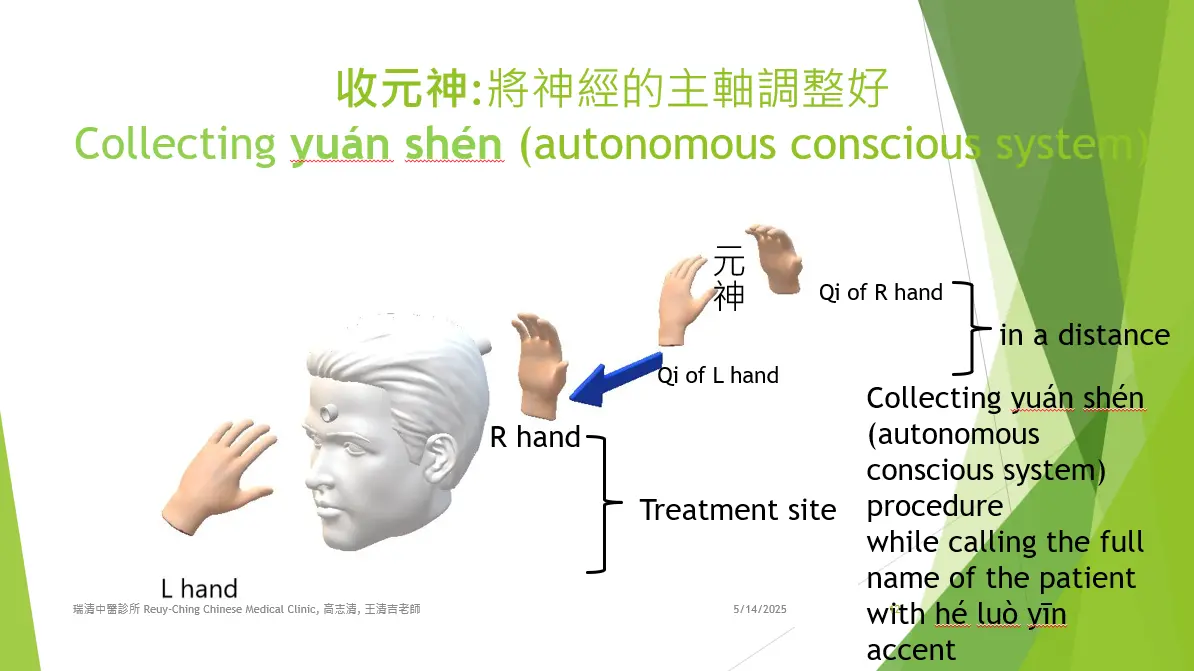
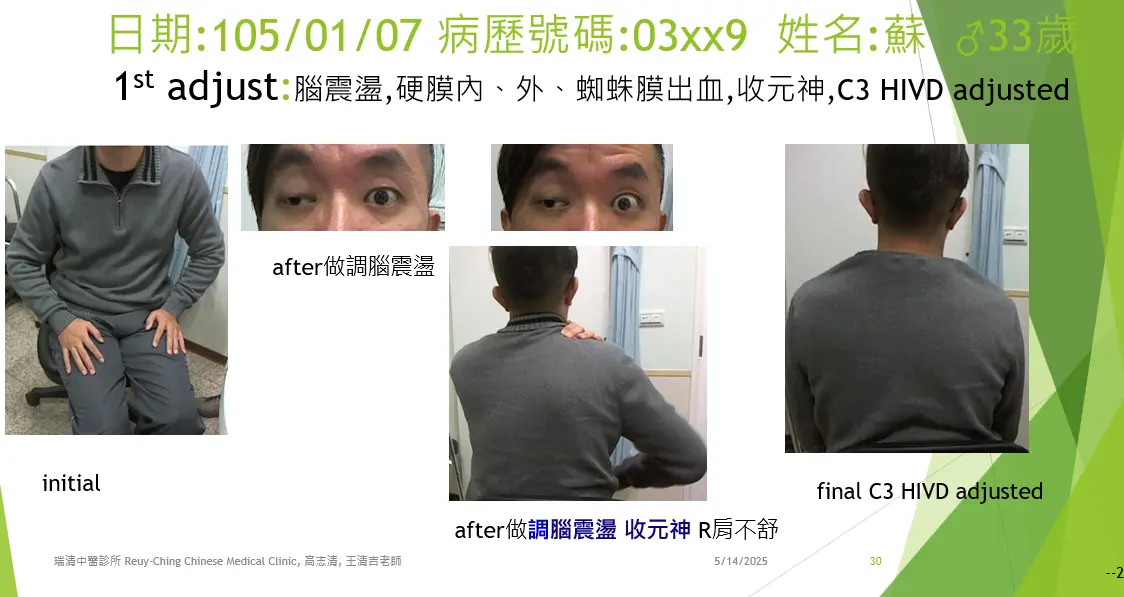
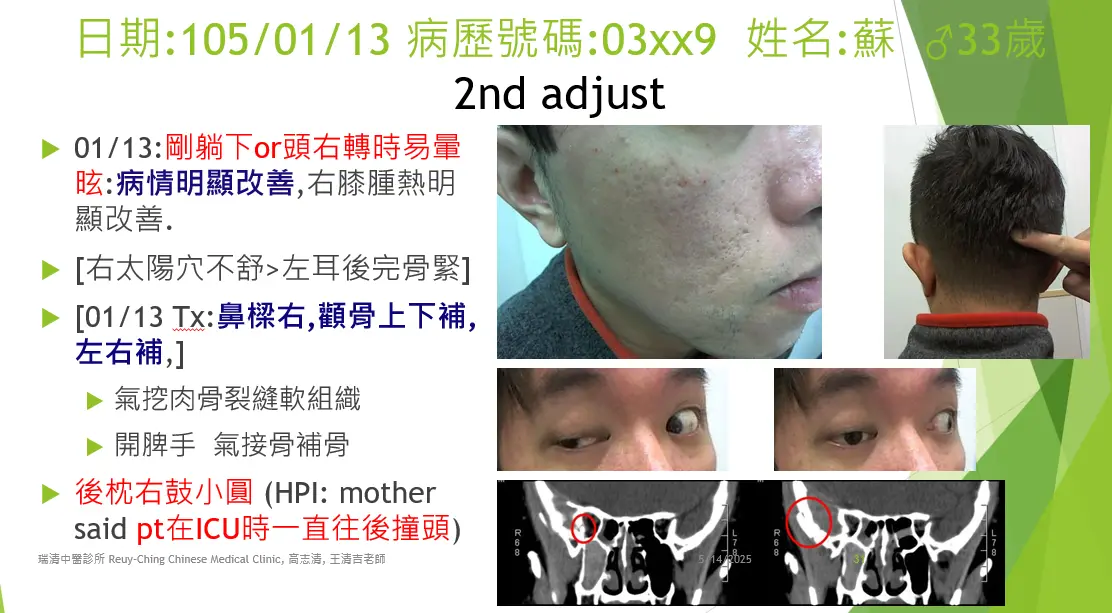
The kāi pí shǒu (開脾手, "open spleen manipulation") technique is applied in these spaces using verbal formulas called hé luò yīn (an ancient Heluo dialect) to help restore the normal positions of nǎo shén (brain spirit), nǎo qì (brain qi), and nǎo xuè (cerebral blood). If parts of the meninges are stuck in skull fissures, they are gently pulled out before repairing the cranial bone cracks. Any adhered tissues are carefully separated using kāi pí shǒu. Additional verbal formulas accompany further kāi pí shǒu treatments to repair meningeal blood vessels. For patients with brain concussion who have lost consciousness or are traumatized by their injury, a procedure called collecting yuán shén (original spirit or autonomous conscious system) is recommended to help restore normal body function.
材料與方法
丹氣醫術作為傳統醫學的一支,歷經多代師徒相傳,但未納入現代醫學課程。經過充分丹氣訓練的醫師能從指尖發出氣,並將氣導入患者眼睛與顴骨之間的狹縫,進入硬膜外、硬膜下或蛛網膜下腔等空間。
在這些空間中做開脾手,配合河洛音口訣,旨在使腦神、腦氣和腦血恢復正常位置。若部分腦膜卡在顱骨裂縫中,要先緩慢拉出被夾住的腦膜,再修復顱骨裂隙。黏連組織也要用開脾手小心分離。隨後,配合更多口訣進行開脾手,以修復腦膜血管。
對於腦震盪且曾失去意識或因事故驚恐的患者,建議施行收元神程序,以幫助身體恢復正常功能。
Results
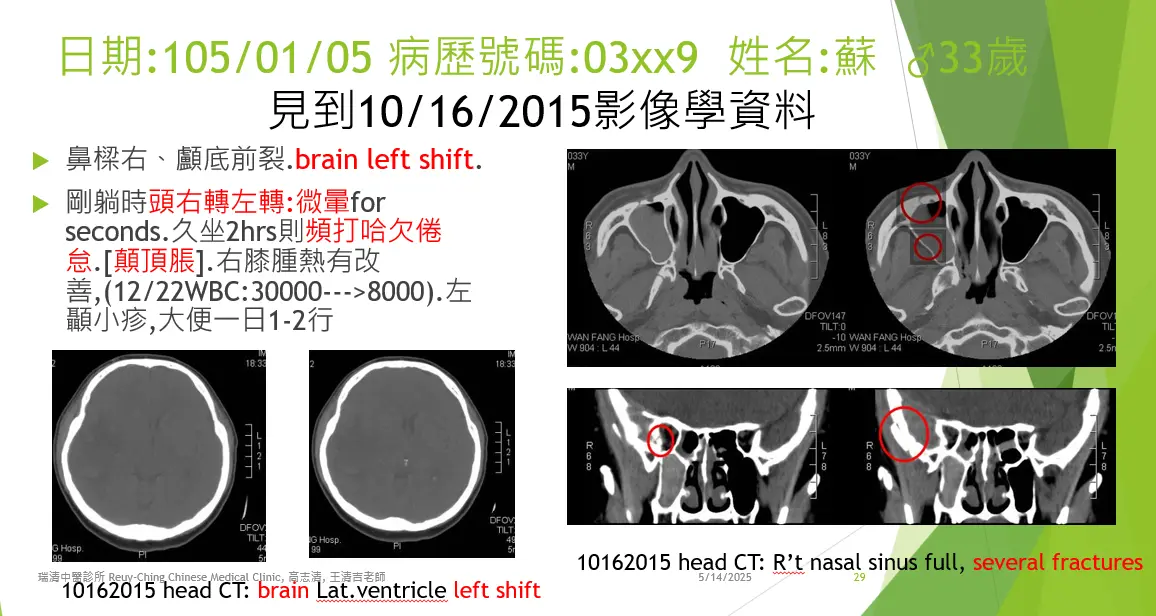
Cases of brain concussion were presented, including chief complaints, prescribed processed herbal medicines, and patients’ subjective changes before and after dān qì therapies. Both doctors and patients reported clear relief of symptoms during clinic visits.
結果
本報告呈現了腦震盪病例,包含主要症狀、所開立的中藥處方,以及患者在接受丹氣療法前後的主觀感受變化。醫師與患者均反映,患者在診療現場明顯感受到症狀緩解。
Conclusion
The remarkable effectiveness of dān qì therapy suggests that the mechanisms behind brain concussion may involve factors beyond what routine imaging can detect.
結論
丹氣療法的卓越療效顯示,腦震盪的機制可能涉及常規影像檢查無法識別的因素。
Keywords: Brain concussion, Dān qì, Kāi pí shǒu, Hé luò yīn verbal formulas, Yuán shén
關鍵詞: 腦震盪、丹氣、開脾手、河洛音口訣、元神